
ECG Educator Blog Junctional Rhythms
Junctional rhythms and tachycardias Premature atrial complexes Occur as single or repetitive events and have unifocal or multifocal origins. The ectopic P wave (called P') is often hidden in the ST-T wave of the preceding beat. (Dr.

Case B7. Third Degree AV Block with Junctional Escape Rhythm. St Emlyn
A junctional escape beat is a delayed heartbeat originating not from the atrium but from an ectopic focus somewhere in the atrioventricular junction. [1] It occurs when the rate of depolarization of the sinoatrial node falls below the rate of the atrioventricular node. [2]
Junctional Escape Rhythm • LITFL • ECG Library Diagnosis
Complete Heart Block with Isorhythmic AV Dissociation (long rhythm strip): Atrial rate ~ 85 bpm; Ventricular rate ~ 42bpm; There is a junctional escape rhythm; As the ventricular rate is approximately half the atrial rate, this rhythm at first glance appears to be second-degree AV block with 2:1 conduction; However, on closer inspection, the PR interval varies with some of the P waves.

Pin on Cardiac Queen
Junctional and ventricular escape rhythms arise when the rate of supraventricular impulses arriving at the AV node or ventricle is less than the intrinsic rate of the ectopic pacemaker. Causes Conditions leading to the emergence of a junctional or ventricular escape rhythm include: Severe sinus bradycardia Sinus arrest Sino-atrial exit block

ECG Educator Blog Junctional Escape
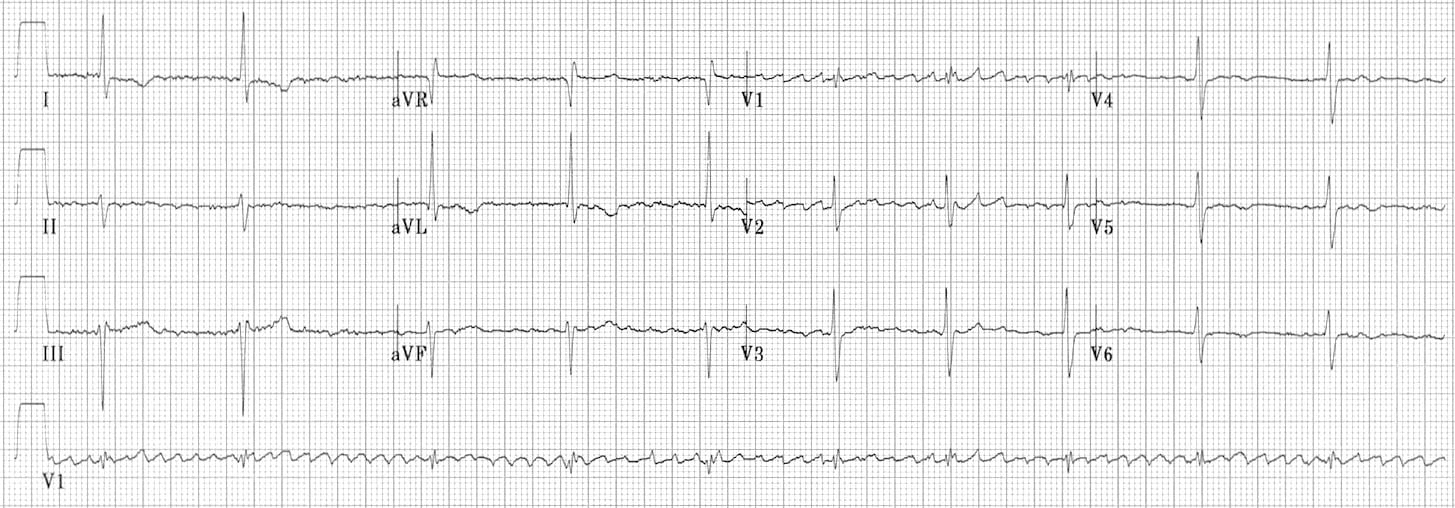
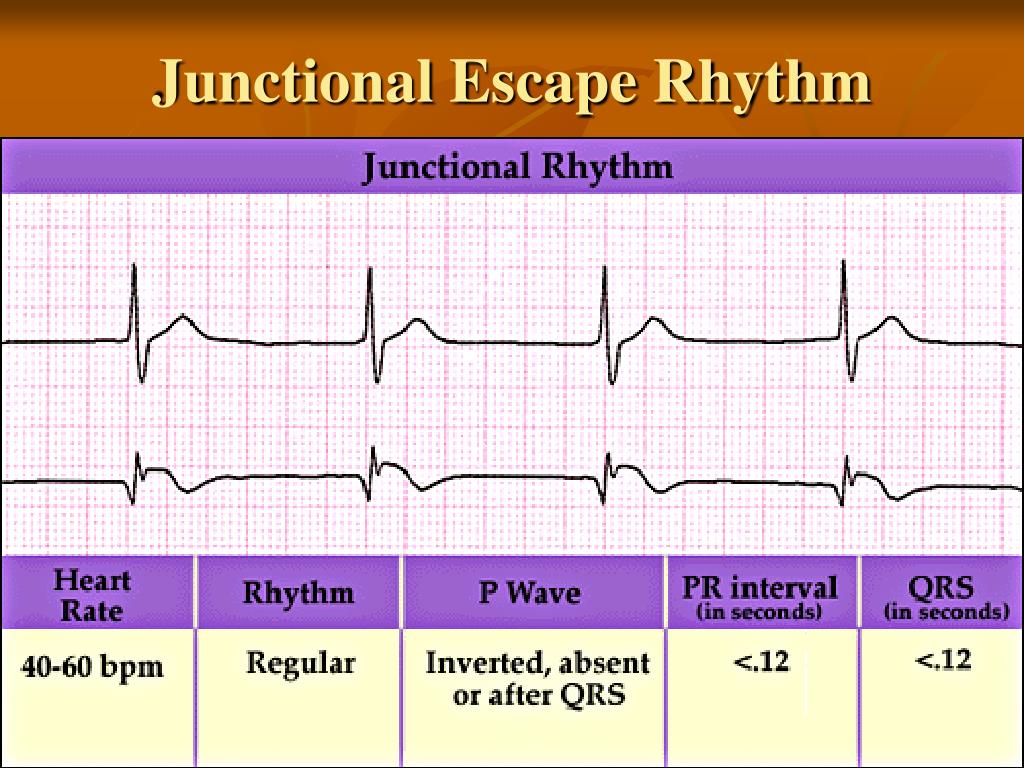
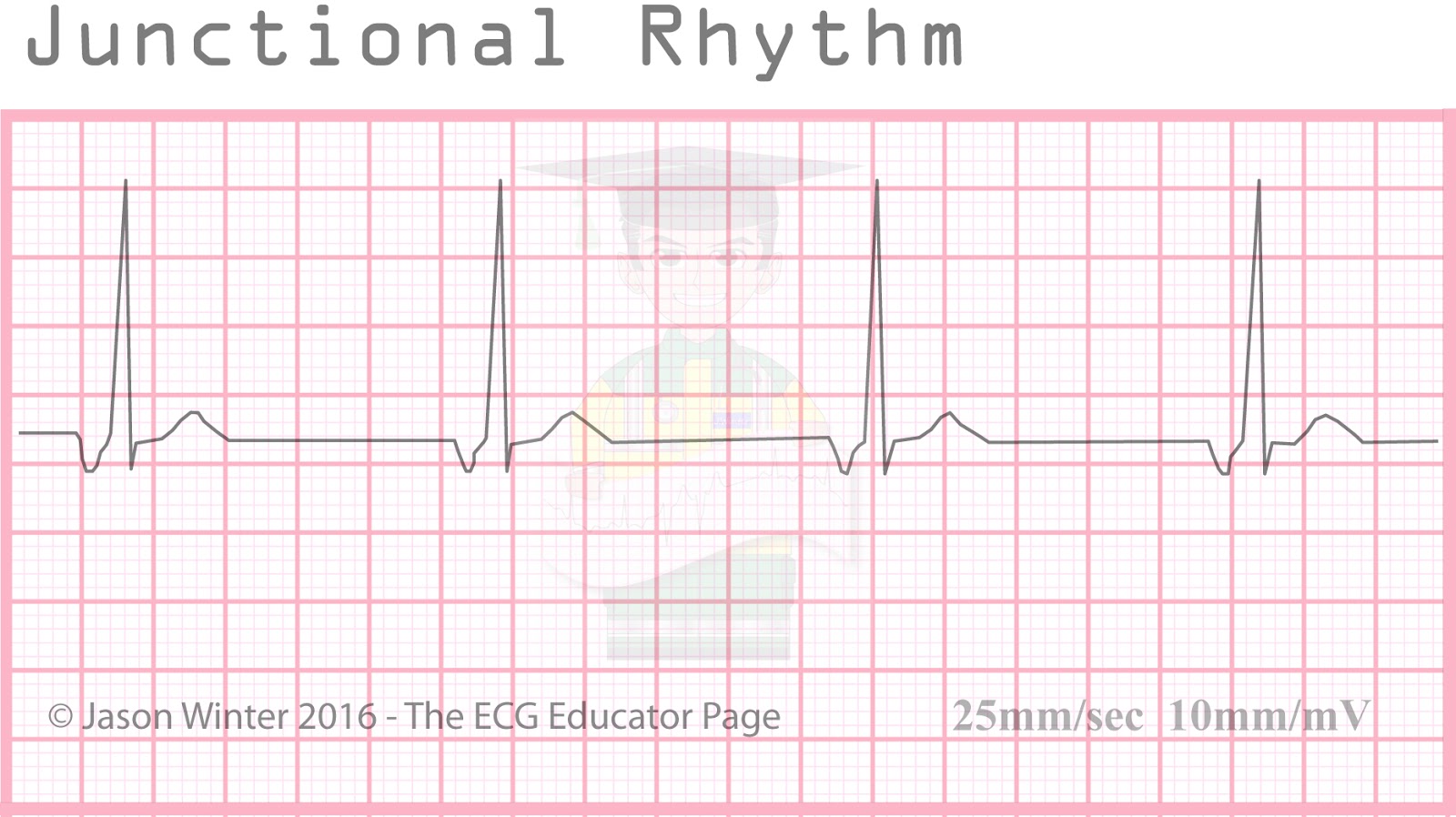
Junctional escape rhythm is a regular rhythm with a frequency of around 40-60 beats per minute. In case of sinus arrest (or any scenario in which atrial impulses do not reach the atrioventricular node), junctional escape rhythm may be life-saving.

PPT Introducing the Junctional Rhythms PowerPoint Presentation, free
A junctional rhythm is an abnormal heart rhythm that originates from the AV node or His bundle. This activity reviews the evaluation and management of junctional rhythm and highlights the role of the interprofessional team in educating patients about their prognosis. Objectives: Outline the risk factors of developing a junctional rhythm.

Float Nurse Practice EKG Rhythm Strips 163
Junctional and ventricular escape rhythms arise when the rate of supraventricular impulses arriving at the AV node or ventricle is less than the intrinsic rate of the ectopic pacemaker. Causes Conditions leading to the emergence of a junctional or ventricular escape rhythm include: Severe sinus bradycardia Sinus arrest Sino-atrial exit block
PPT ELECTROCARDIOGRAM PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID297761
A central core of pacemaking cells ( P cells) that produce the sinus impulses. An outer layer of transitional cells ( T cells) that transmit the sinus impulses out into the right atrium. Sinus node dysfunction can result from either: Failure of the P cells to produce an impulse. This leads to sinus pauses and sinus arrest.

Junctional bradycardia EKG examples wikidoc
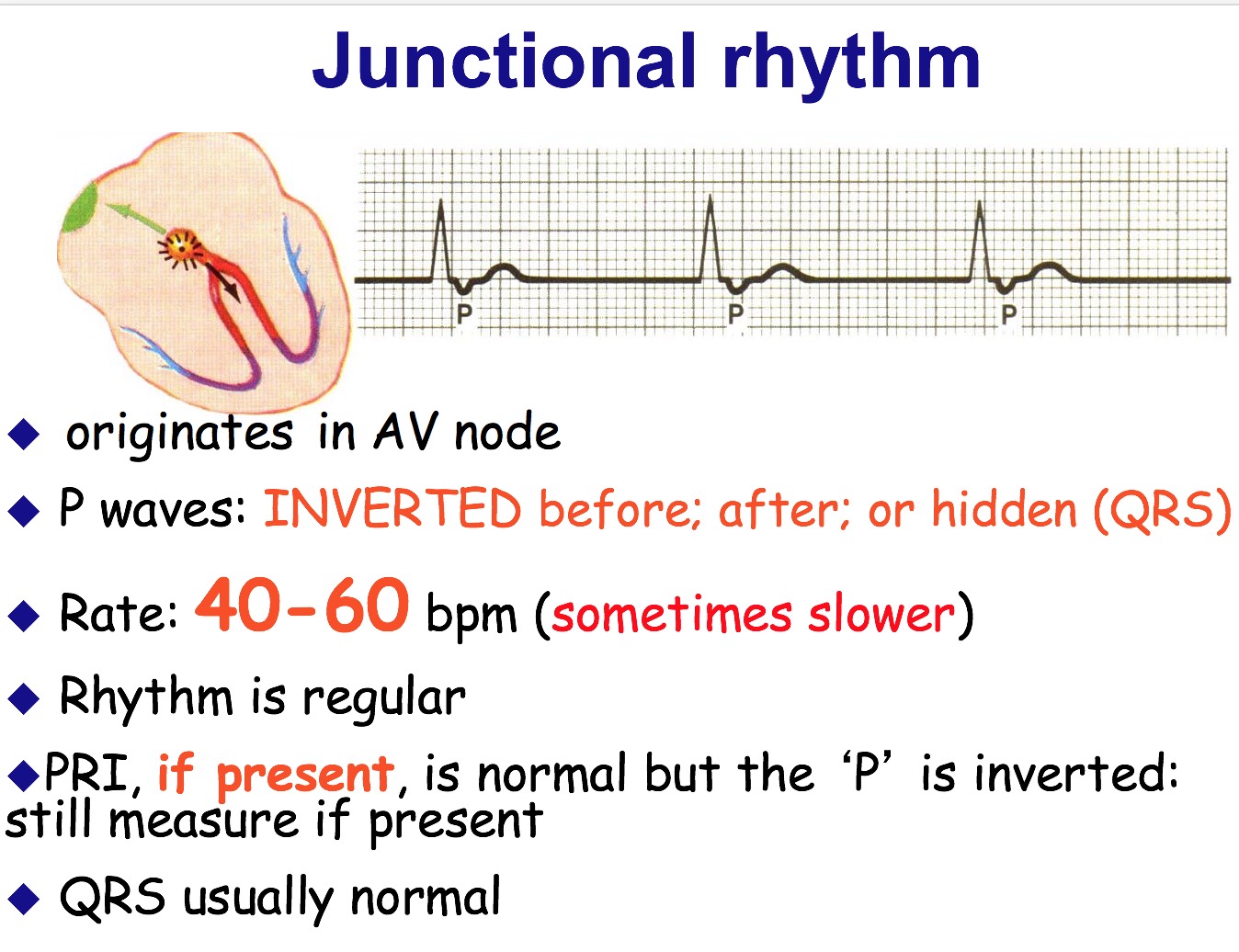
These are called junctional escape beats . Junctional rhythm. Junctional rhythm (Figures 8-10, 8-11, 8-12 and 8-13 and Box 8-2) is an arrhythmia originating in the AV junction with a rate between 40 and 60 beats per minute. Junctional rhythm is the normal rhythm of the AV junction. Junctional rhythm can occur under either of the following.

Junctional escape beats
Junctional rhythm is a type of irregular heart rhythm originating from the atrioventricular junction. Learn more about it, including its types, symptoms, causes, and more.. Junctional escape.
Junctional Rhythms
When the sinus rate falls below the discharge rate of the AV node, this becomes the dominant pacemaker, and the result is called a junctional escape beat. If the rate from both the SA and AV node fall below the discharge rate of ventricular pacemaker cells, a ventricular escape beat ensues. [citation needed]
ECG Educator Blog Junctional Rhythms
This escape mechanism, with a rate of 40-60 beats per minute, produces a narrow QRS complex because the ventricle is depolarized using the normal conduction pathway. An accelerated junctional rhythm (rate >60) is a narrow complex rhythm that often supersedes a clinically bradycardic sinus node rate (see images below).

PPT Junctional Dysrhythmias PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Overview What is a junctional rhythm? A junctional rhythm is a type of arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat). If you have a junctional rhythm, your heart's natural pacemaker, known as your sinoatrial (SA) node, isn't working as it should. Your SA node sends electrical signals that control your heartbeat.

JUNCTIONAL ESCAPE RHYTHM
A junctional rhythm is usually between 40 - 60 bpm, with a narrow QRS. Ventricular escape rhythms are usually less than 40 bpm and with wide QRS complexes. T his ECG will be a little challenging on this front, because the rhythm has some characteristics of junctional rhythm and of ventricular rhythm. Read more.

Float Nurse Practice EKG Rhythm Strips 201
Junctional escape beats and junctional escape rhythm are seen commonly in normal children, especially on ambulatory recordings during sleep, 1,2,81 but are less common on routine ECG in pediatric patients who are awake and at rest. It is usually seen in two clinical situations in pediatrics.
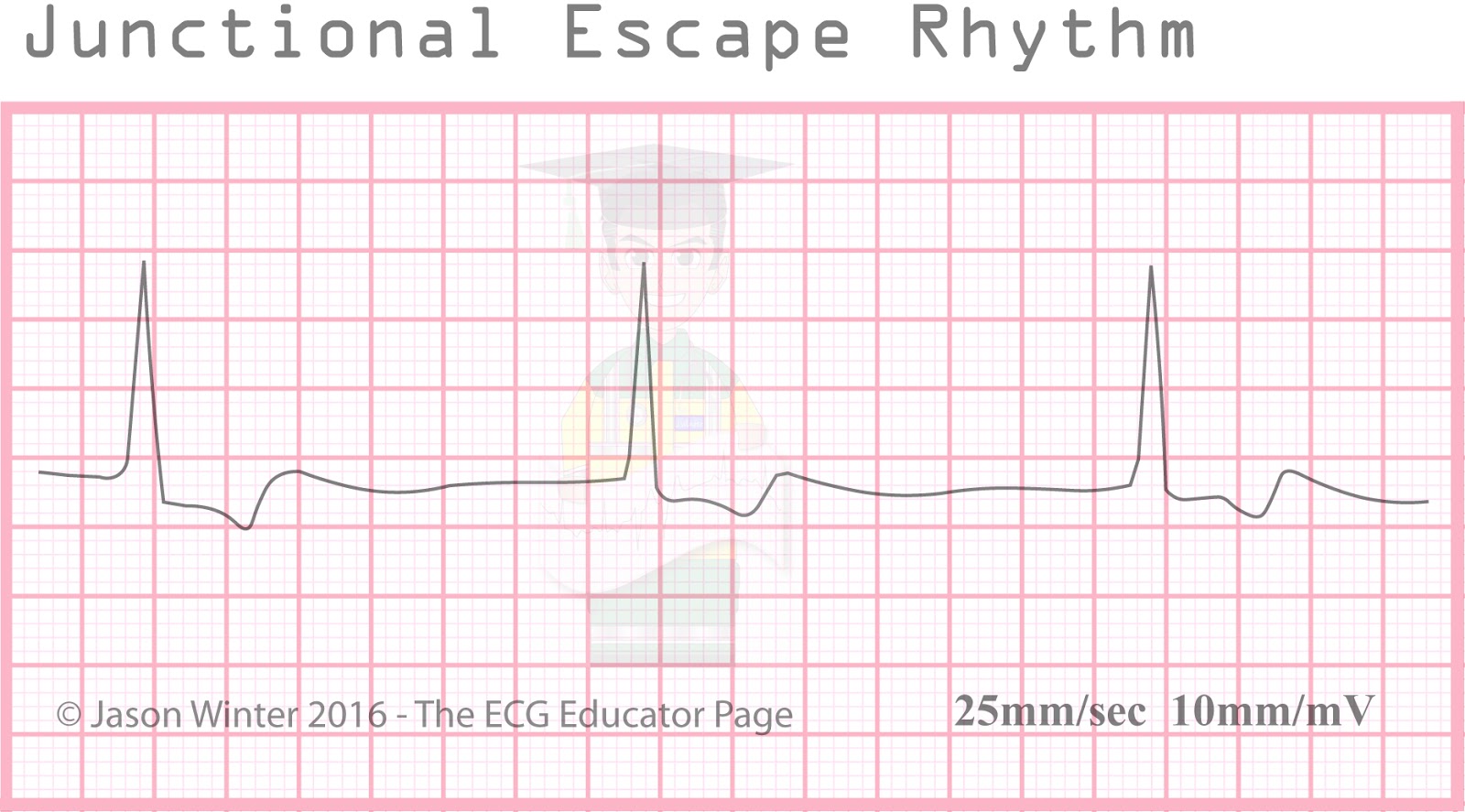
ECG Educator Blog Junctional Rhythms
A junctional rhythm is a type of abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia. It is usually not serious, although it can be associated with heart inflammation or recent heart surgery. It happens when the atrioventricular (AV) node or "His bundle," both of which are electrical signals that help control your heartbeat, isn't working properly.